Donaties

St. Vishnuh-Genootschap
(KvK: 56636814)
Voor inschrijving en donaties kunt U e-mailen naar vishnuh-genootschap@hotmail.com o.v.v. inschrijving lidmaatschap/ donaties.
FND. Vishnuh-Society
(KvK:56636814)
For registration and donations, you can e-mail to vishnuh-genootschap@hotmail.com stating membership/donations.
Pijet-Massage-Nerve-Pressure-Points-Doctrine
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form by means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the written permission of the publisher.
PIJET (Read Piedjet)

JAVANESE
MASSAGE NERVE PRESSURE POINTS DOCTRINE
Pain relief
through Pijat techniques
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
Pain treatment, local paralysis and pain relief by applying pressure with the fingertips on the nerve points of the body parts to be treated.
Everyone who has the necessary knowledge of anatomy and physiology is able to bring a lot of relief to pain sufferers by applying the nerve pressure point theory of the Vishnuh-Society.
However, the method and rules for the pressure points as stated in this book must be followed exactly, so that the pain area to be treated is carried out safely and easily. But the nerve pressure theory also has its limitations, and we must be aware of this so that people do not think that it is a remedy for all kinds of ailments.
Remember; the Pijet techniques of the Vishnuh-Society is not a magic tool that can cure all kinds of physical discomfort.
In this chapter, attention is paid to pain relief and pain relief through the body, including ear, leg, face, back and other body parts by applying pressure with the fingers on the body and by means of massage techniques (Pijet = Javanese word for pressure point massage.)
WHAT IS PAIN?
Pain is originally an alarm signal from the human body. It is very important to know and understand the real causes of pain when it comes to controlling pain so that the pain can be successfully treated. Pain can arise from a large number of causes.
In the nerve pressure point theory of the Vishnuh-Society, the practitioner is taught a number of effective treatment methods. This is sufficient if you know the rules for application and adhere to them exactly. In addition, you can look up the points when you need them. The human body has the ability to use stimuli as optimally as possible and stimulating a nerve pressure point helps to improve both high and low blood pressure.
Another point corrects a slow or accelerated heartbeat and others increase the number of blood corpuscles and promote the absorption of dead tissue residues and others through white corpuscles. It is also possible here to cure a sick ankle by massaging the nerve points of the healthy leg to heal the other leg.
To successfully relieve a painful body area, you must press the indicated nerve points with your thumb and forefinger. At the same time, you feel how electrostatic energy acts on that location. The bio-magnetism in the body that is disturbed by the pain is restored because the pressure on the painful area stimulates the brain to make encephalin (natural pain anesthetics) in the body. This method of pain relief can be used indefinitely.
The application of finger pressure from nerve points to the body successfully causes a reduction in pain, an increase – decrease in paralysis, etc.
The inhibitory and beneficial effect of finger pressure on the body.
Deep penetrating pressure on muscles and tendons has an inhibiting effect on pain. Each action has a reaction, and the body, and will respond to stimuli at various heights, depending on the location, duration, and nature of stimulation.
It is also very important not to forget that the human body is the actual vital factor in finger pressure treatment. The location, duration, and method (e.g., needle, finger pressure, and electrical stimulus) determine the simulation of sedation or anesthesia of the body.
The nature of the response to the finger pressure determines the healing, anesthesia and/or paralysis. The applied finger pressure acts as a stimulus, and if the finger pressure is held for five to ten seconds, anesthesia or paralysis will occur in the body.
There is also a disadvantage to this method with finger pressure because irritations and/or changes can occur at every nerve point and in adjacent parts of the organism even after treatment for pain relief.
All nerve pressure points of the body are closely related to body organs and functions. In addition, the individual points on the pinna, face, hands, and legs are related to specific reflex effects of the body.
Furthermore, in the case of rheumatic pains and muscle disorders, the more distant nerve points with relation to the focal points should be treated instead of only the relevant pains.
It must be known that the blood channels of the body are related to the nerves, blood vessels and bodily substances (also body juices.)
The nerve points are usually around the painful area so that incorrect use of the nerve pressure points is very small. Farther-away points of the painful spot can be combined with local nerve points.
GENERAL
Before someone is treated, he or she must first relax for 15 minutes.
One should apply pressure to the nerve points of the body, usually in the painful or farther-away area, with a circular motion with the thumb and index finger.
The moment that pressure is applied to the nerve point with the index finger, pain may occur for a moment, after which the feeling of pain will express itself in a feeling of warmth. In areas with low muscle tissue, the skin around the pressure point should be carefully tended before treatment is started.
In places where the subcutaneous tissues are loose or wrinkled, the skin must be smoothed.
The pressure on the nerves can be carried out in two ways, namely obliquely and straight. The painful areas to be treated must be treated with finger pressure for at least half an hour.
The finger pressure should be deep enough to cause a warm feeling. The pressure exerted by finger and thumb can be painful, but it is tolerable for the person concerned.
In addition, it is possible to stimulate different nerve points with finger pressure simultaneously.
The pressure depth should be varied by increasing the pressure on one side and reducing the pressure on the other area.
It is certainly useful to use variable pressure at a point. The pressure on the body should be slowly increased on the body for ten to twenty seconds and then reduced again.
Continuation of Treatment
Treatment should be continued until the person concerned indicates that the pain has subsided.
Never exaggerate, otherwise the person involved may also get bruising from the pressure on the treated areas, which is obviously not the intention.
Apply enough pressure, as needed, to suppress the feeling of pain. Make sure that the person to whom control is applied during the treatment is completely relaxed.
Before moving on to treat someone, the person concerned must be observed intuitively. You should locate the pain area with sensitive hands.
The nerve pressure points doctrine is a possibility to remedy disorders and pains in a variety of areas through natural means. The patient’s treatment should be repeated more often until the patient’s pain has completely disappeared.
Furthermore, the person to be treated must voluntarily want to cooperate in his treatment and must relax completely, because if one is afraid of what is going to happen, he may even worsen the painful condition; but spiritual determination (relaxation) can suppress the consciousness of even severe pains.
In dragging cases, a large gap should be kept between treatments, so that the body can recover after the previous treatment. For instance; a treatment every other week, during which the patient has a week to relax physically.
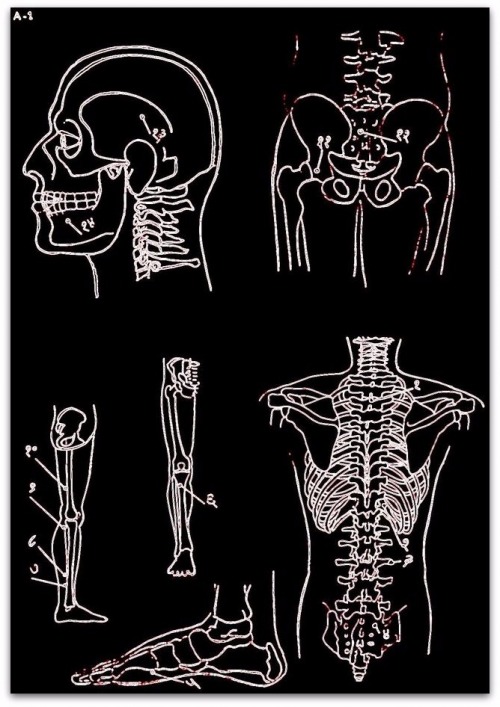
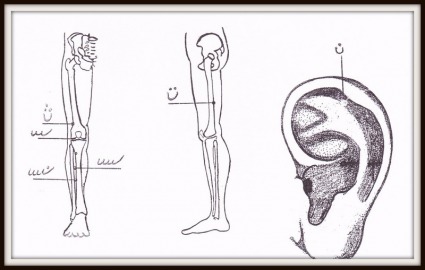
NERVE PRESSURE POINTS ON THE EARCUPS PART 1
A. Toe C. Adrenal E. Knee G. Butt I. Rump vertebrae K. Neck M. Shoulder | 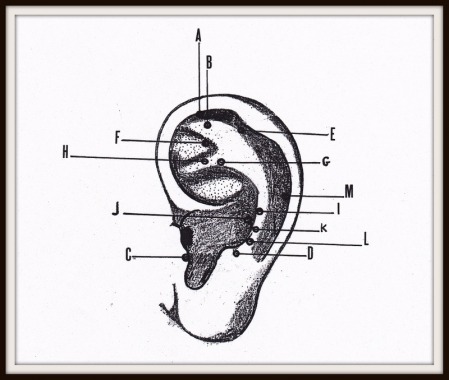 |
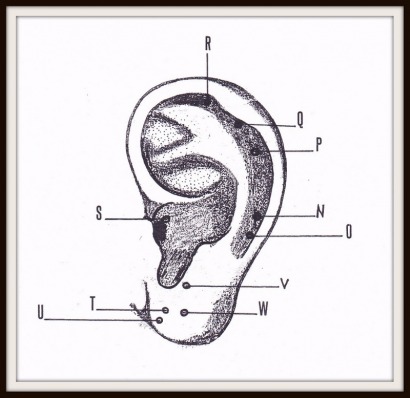
NERVE PRESSURE POINTS ON THE EARCUPS PART 2
PART 2
N. Shoulder joint
|  |
NERVE PRESSURE POINTS ON THE EARCUPS PART 3
PART 3
AA. Pharynx CC. Small intestine EE. Gallbladder GG. Liver II. brainstem | 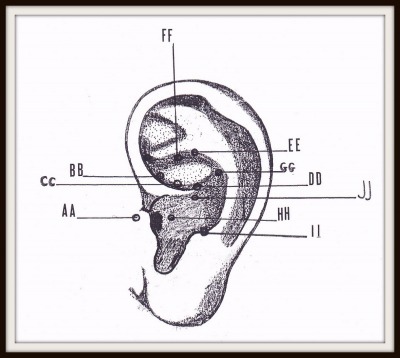 |
NERVE PRESSURE POINTS ON THE BACK PART 4
PART 4
A. Nerve pathways that relate to each other, and those serving as a heat conductor (anesthesia or paralysis) B. Gallbladder C. Liver D. Urinary bladder E. Liver F. Urinary bladder | 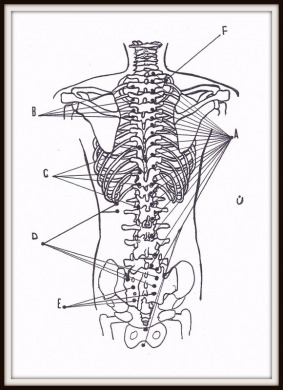 |
NERVE PRESSURE POINTS ON THE BACK PART 5
PART 5
G. Large intestine H. Small intestine I. Urinary bladder J. Maag * K. Milt L. Stomach * | 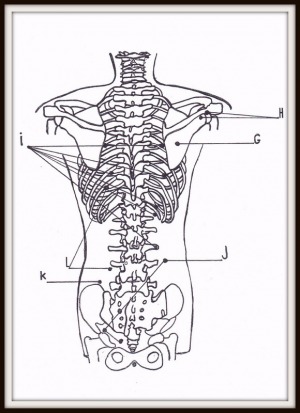 |
NERVE PRESSURE POINTS ON THE LEG AND FOOT PART 6
PART 6
A. Kidney – B. Kidney C. Stomach – D. Gallbladder E. Liver – F. Urinary Bladder G. Spleen – H. Gallbladder I. Heart – J. Urinary Bladder K. Ancle – L. Ancle M. Liver – N. Urinary Bladder O. Stomach – P. Milt Q. Liver – R. Stomach S. Liver – T. Stomach U. Gallbladder V. Liver – W. Milt X. Kidney – IJ. Kidney – Z. Liver Often there are various pressure points that will be the same in this group; A, B, X & IJ represent the Kidneys; C, O, R & T the Stomach; D, H & U the gallbladder; E, M, Q, V & Z the Liver; F, J, and N, the (urinary) bladder; G, P & W the Spleen; K & L de Ancle. AA. Urinary Bladder BB. Milt CC. Gallbladder DD. Kidney EE. Stomach * FF. Stomach * GG. HH spleen. Liver II. Liver* |
|
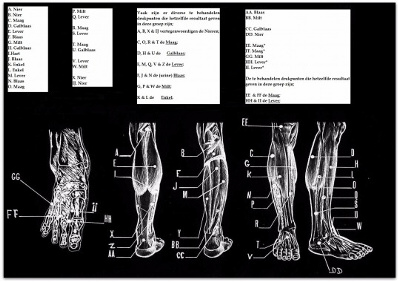
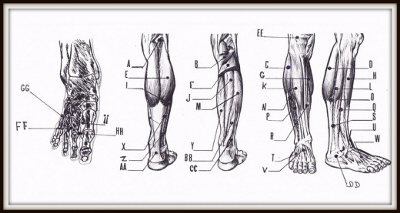
NERVE PRESSURE POINTS ON THE LEG AND FOOT
PART 7
1. Urinary bladder 5. Gallbladder which are the same in this group; 1, 10 & 12 the urinary bladder; 2, 13 & 15 the Liver; 3, 6 & 9 the Stomach; 4 & 5 of the gallbladder; 7, 11 & 17 the Kidney; 8, 14 & 16 the Spleen. | 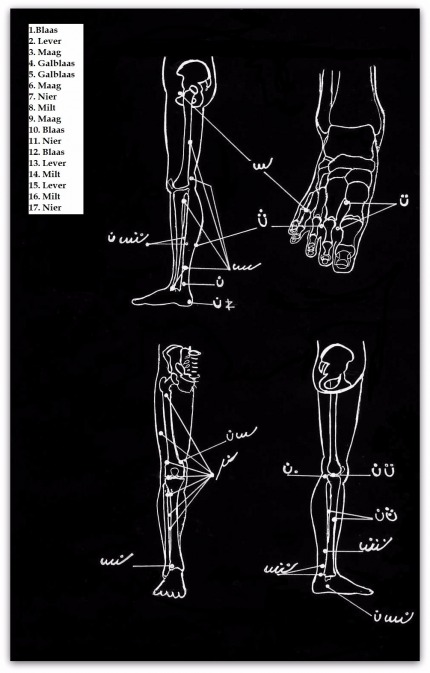 |
RHEUMATIC
TREATMENT TO THE FOOT
PART 8
Leg and foot: 2. between the 1st and 2nd toe; 3. between the 2nd and 3rd toe; 5. between the outer nodule and Achilles tendon; 10. between the outer ankle and the Achilles tendon; 17. In the middle between the tip of the inner ankle – and Achilles tendon. Through the nerve tips on the ear, rheumatic treatment is also possible. On the ear; AB, C & D. Arthritic pain treatment by finger pressure should be done carefully. The painful place to massage must be done with rotating movements. The patient must be in a relaxed state during treatment. One must treat the patient at least twice a week and never massage for more than an hour. | 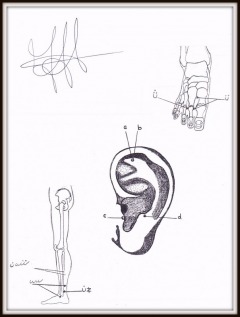 |
RHEUMATIC
TREATMENT ANKLE
PART 9
On Ankle 4. Above the top of the inner ankle bump; – of the inner ankle and the Achilles tendon; – at the center of the inner ankle bump; | 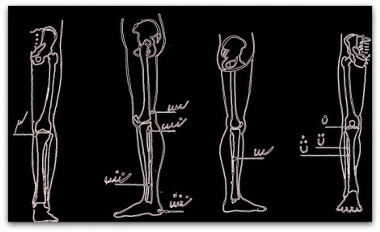 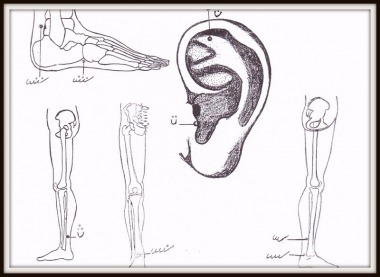 |
RHEUMATIC
PAIN TREATMENT AT THE KNEE JOINT
PART 10
On the leg – just below the knee paw; 3. just below point 2; 5. at the thigh surface just above the lower femur head; 7. The tip above the outer ankle nodule, straight for the calf 9. The tip of the knee cavity with a bent knee. Choose six (6) to eight (8) points from the list for knee treatment. |
But do not pick out points in a spontaneous painful place/ tumor or a swelling. If necessary, circle the painful site and use the nearest nerve points. The other knee can be treated to remove the pain. This treatment is suitable for removing pain in the loins and the rest of the body. |
TREATMENT
OF NERVE PAIN IN THE KNEE
PART 11
To the ear:
1. knee joint;
At the Bone:
2. the point above the knee crease;
3. the tip above the knee disc;
4. The point just above the tibia;
5. The point between the front shin muscle and tibia, just below the knee paw;
6. The point below 5.
The painful place to massage should be done with slow-moving motion. Do not massage the painful place for more than 5 minutes.
Thus says, the doctrine of Vishnuh:
“ Whoever wants to enjoy life must open his mind first, and no one is entitled to tell the other how to live. But the man makes sense to enjoy life because realizing that everything in life has a duration, except life itself.”
RHEUMATOID
PAIN TREATMENT OF HIP AND OTHER GENERAL PAIN
PART 12
The ear : 1. But point The lower back: 3. Liver. The point on the bend of the groin and femur head ader The gallbladder: The leg: The hip joint: 6. Gallbladder These treated nerve tips are suitable for controlling general pain. Also, these points can be combined successfully with other nerve points in general. |
GENERAL
PINE TREATMENT TO THE LEG
PART 13
The foot: 1. Urinary bladder: The tip right below the outer ankle nodule, in the dungeon. The leg: 2. Stomach: The highest point of the rub, the point above the connective tissue between the 2nd and 3rd toes. 3. Stomach: The point below the knee joint and shin bone tip. 4. Stomach: knee-eye point. 5. Stomach: The tip above the knee and the knee disc. 6. Stomach 7. Stomach 8. Gallbladder: The point where the outer ankle nodules meet each other. 9. Gallbladder: The tip above the outer ankle nodule, at the edge of the calf and the long and short calf muscle. 10. Gallbladder 11. Gallbladder The painful place to be massaged should be done with slow rotating motion. Do not massage the painful place for more than 5 minutes. | 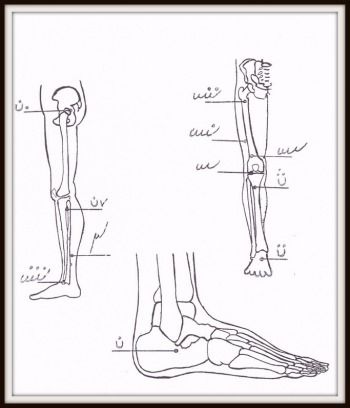 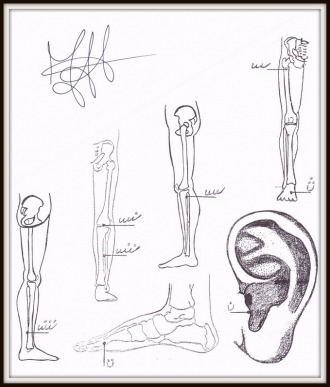 |
INCESSANT PAIN
TO THE UNDERLEG
PART 14
The ear:
1. Adrenal
gland
The foot:
2. The
spleen: the middle of the leg
The leg:
3. Liver: The point in the corner between the 1st and 2nd middle leg.
4. Stomach: At the bottom of the symphysis pubis.
5.
Gallbladder: in the pit of the small calf head.
6. Urinary bladder: The center of the knee cavity.
7. Urinary bladder: the point below the knee pleat.
8. The Melt: The tip of the upper tip, of the inner ankle bump.
In total,
this book (PIJET = Javanese nerve point massage) includes 35 chapters including
a. Nerve
Points create materials for sugar and other disorders of the blood cells
b. Pain
control in the loins
c. Pain control in the spine
d. Pain control on the wrist
e. Pain control in the elbow
f. Pain control in the shoulder
g. Pain control in the throat
h. Pain control in hand and fingers
i. Pain control in the jaw
j. Pain relief against headaches
k. Pain control in the forehead
l. Pain relief childbirth pains
m. Pain Relief of Migraine Headache
n. Pain control crown of the head
o. pain relief menstrual pain
p. general nerve points of the body
q. Nerve pressure points on the leg and foot
r. Javanese Glossary of the body